Uses of urea
Urea is the world's most commonly used nitrogen fertilizer and indeed more urea is manufactured by mass than any other organic chemical. Containing 46% N, it is the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizer, and is readily available as free-flowing prills (granules). It is the cheapest form of nitrogen fertilizer to transport and it is also the least likely to 'cake'. It is therefore favoured in developing countries.
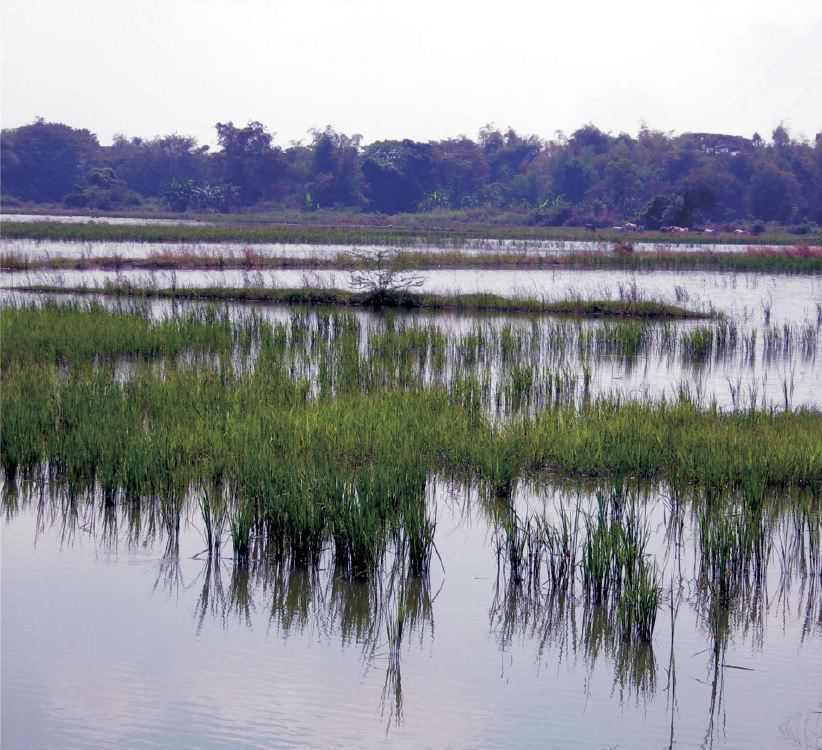 |
Figure 1 This rice paddy field in Thailand has been treated with urea, the nitrogen-containing fertilizer that is most used in developing countries. By kind permission of Kim Dixon. |
While over 90% of urea produced is used as a fertilizer, it has other uses, which include the manufacture of the melamine, used in melamine-methanal resins. Urea itself also forms important resins.
An increasingly important use of urea is in reducing air pollution from diesel engines in cars, buses and lorries. Diesel engines run at high temperatures and nitrogen and oxygen, from the air, are able to react together under these conditions to produce high concentrations of nitric oxide. One way to remove this pollutant is to allow it to react with ammonia to form nitrogen.
However it is not possible to use ammonia directly as it is too volatile and is poisonous. Instead a solution of urea in water is injected into the hot gases emerging from the engine in the exhaust. Urea is thermally decomposed to ammonia and carbon dioxide. This is the reverse of the process used to make ammonia:
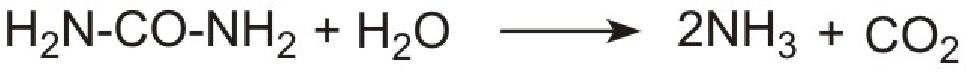
Unlike ammonia, urea is safe and easy to handle.
The products, ammonia and carbon dioxide, together with the exhaust gases, are passed immediately over a catalyst in the exhaust system. Ammonia reduces the oxides of nitrogen (mainly nitric oxide), formed in the combustion processes, to nitrogen. The process is complex but the overall reaction can be represented thus:
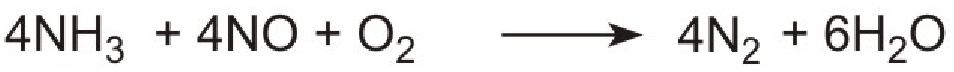
The system is known as Urea SCR (urea-based selective catalytic reduction) and can reduce pollution by nitrogen oxides to almost zero.

Annual production of urea
| World | 151 million tonnes |
| Europe | 10 million tonnes |
| North America | 10 million tonnes |
| Asia | 94 million tonnes |
| FSU | 11 million tonnes |
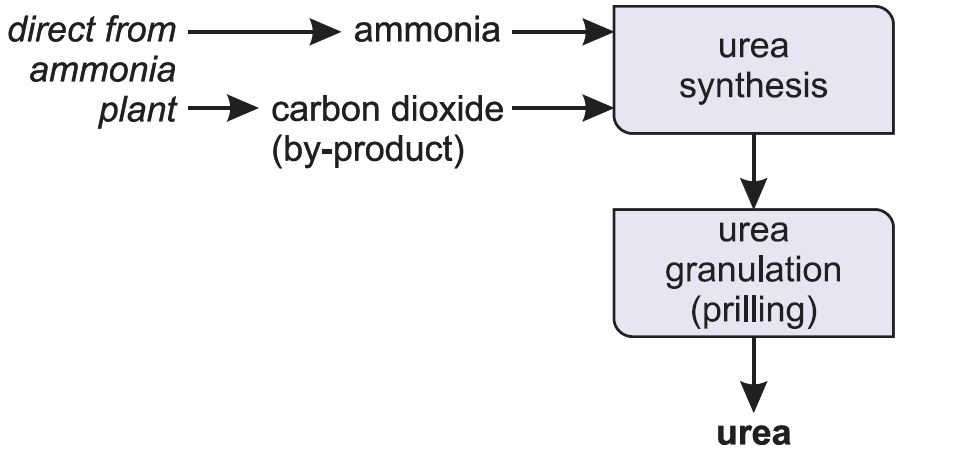
Manufacture of urea
Ammonia reacts with carbon dioxide to produce urea. Urea is always manufactured close to an ammonia plant (Figure 5).
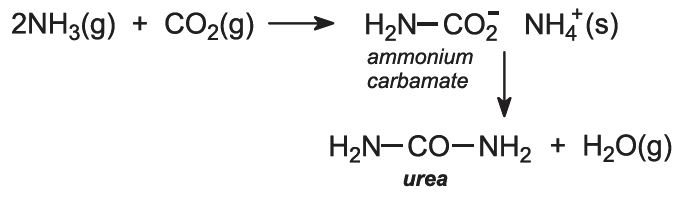
Ammonia and carbon dioxide are heated together at 450 K and 200 atm pressure. First ammonium carbamate is formed, which rapidly decomposes to form urea:

Figure 5 An aerial view of a large plant in Alberta, Canada, in which ammonia is synthesized
and then converted to urea.
By kind permission of Agrium Inc.
Much of the urea is prilled (Figure 6) and sold in that form.
|
Figure 6 These small spheres of urea are known as prills. The prills are formed by spraying molten urea down a tower up which air is pumped. They are slightly smaller than urea sold as granules and are particularly useful when the fertilizer is being applied by hand. By kind permission of Agrium Inc. |
 |


REALATED TAGS: WHAT IS UREA,UREA TO PROCUDE,UREA FERTILIZERS,NITROGEN BASED FERTILIZERS,MAKING UREA,FORMULATIONS OF UREA,MANUFACTURING UREA,HOW TO MAKE UREA,HOW TO USE UREA,WHERE TO USE UREA,UREA MAKING,COMPOSITION OF UREA.
SOLVER CHEM

|
|

|
|

|
|